Sleep apnea is a sleeping disorder that can lead to serious complications. It causes individuals affected to momentarily stop breathing for short periods of time throughout the night. This leads to inefficient sleep cycles, which can wreak havoc on the body and mind over time. Sleep apnea disproportionately affects older males, but individuals of any age, race, and gender can experience it. Due to the seriousness of long-term complications associated with this sleeping disorder, it's important to seek treatment early. Here, we’ll discuss some of the causes, symptoms, and effects of sleep apnea on the body.
Different Types of Sleep Apnea
There are two primary types of sleep apnea, obstructive and central. Both of these result in periodic disruptions to your breathing and require treatment.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea is the most common type of sleep apnea. It’s caused when your airway becomes blocked while sleeping. The throat muscles become too relaxed, which narrows the airway passage and can cause either a partial or complete obstruction. This puts excess strain on your diaphragm and chest muscles as they work to force air through your lungs. Individuals usually resume breathing after a loud gasp, choke, or, in some cases, body spasm. This can repeat anywhere from five to 30 times or more each hour throughout your sleeping cycle, thus severely impairing your quantity and quality of sleep.
Central Sleep Apnea
Central sleep apnea occurs when there’s a disconnect between your brain and your respiratory control center. The neurons fail to fire, and muscles don’t receive consistent signals to breathe. CSA is directly related to an individual’s central nervous system. There are no blockages or obstructions in this type of sleep apnea, and it is much less common than OSA.
While rare, individuals can also experience something called complex sleep apnea syndrome. This describes someone who has both obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea, which can worsen symptoms. If you think that you may have any type of sleeping disorder, contact your doctor as soon as possible.
Sleep Apnea Risk Factors
There are several different factors that can increase your risk for developing sleep apnea as you age. One of the biggest indicators is body weight. Obesity drastically increases your risk of developing sleep apnea, as the fat deposits around your upper body can put stress on your airways and lead to obstructions. Some other risk factors include:
- Age – the risk of sleep apnea increases as you age.
- Gender – men are two to three more likely to suffer from sleep apnea.
- Neck Circumference – individuals with thicker necks tend to have narrow airways, increasing the risk of sleep apnea.
- Genetics– having family members with this sleeping disorder increases your risk.
- Smoking – smokers are three times more likely to experience sleep apnea.
- Airways– the size of your airway can influence the onset of sleep apnea.
- Congestion – individuals who have difficulty breathing through their nose experience higher rates of sleep apnea.
- Medical Conditions – certain conditions can increase your risk. Some of them include congestive heart failure, type 2 diabetes, hormonal disorders, lung diseases, high blood pressure, Parkinson’s disease, and more.
- Substance Use– individuals who use alcohol, sedatives, narcotics, or tranquilizers are at a higher risk for sleep apnea.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Both types of sleep apnea can present similar symptoms and oftentimes the first indication of a problem is recognized by your bed partner. If either of you notice any of the following, seek help from your doctor. Common signs of sleep apnea include:
- Snoring
- Restlessness
- Frequent waking
- Sudden awakenings with gasping, spasms, or choking
- Dry mouth upon waking
- Sore through
- Daytime fatigue
- Sleepiness
- Cognitive impairment
- Mood disturbances
- Irritability
- Night sweats
- Sexual dysfunction
- Morning headaches
- Frequent nighttime urination
The Effects of Untreated Sleep Apnea on Your Body
Sleep apnea is considered a serious medical condition, as it has a substantial effect on various parts of your body. Some of the most serious complications of untreated sleep apnea include the following:
Fatigue
One of the biggest effects of sleep apnea on the body is daytime fatigue. Since you’re not getting enough REM sleep throughout the night, your body isn’t properly rested and restored when you wake up. This can affect your mood, cognitive ability, and physical activity level. This type of fatigue is unlikely to go away each night, even if you spend more hours in bed than normal. The only way to combat this is to treat your sleep apnea.
Memory Loss
During a healthy sleep cycle, your brain filters out waste products, processes memories, and prepares for new information. Sleep apnea can contribute to mild cognitive impairment, or memory loss and forgetfulness. Severe forms of this are seen in dementia, but not everyone who suffers from mild impairment will progress that far. While these complications tend to affect older individuals, sleep apnea can cause a more rapid decline in memory functioning. Treatment can help prevent this or delay cognitive decline.
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a term that refers to a group of conditions that have been medically linked to obstructive sleep apnea. This increases your risk of stroke, heart disease, diabetes, and other complications. Individuals who suffer from metabolic syndrome have at least three of the following conditions:
- High blood sugar
- Low levels of HDL (good) cholesterol
- High levels of triglycerides
- High levels of abdominal fat
- High blood pressure
High Blood Pressure
The constant cycle of waking up throughout the night puts a lot of added stress on your body. This activates hormone production, which increases blood pressure. The lack of oxygen being inhaled due to obstructions can also exacerbate this issue. Sleep apnea is even more problematic for individuals already suffering from high blood pressure.
Heart Disease and Stroke
Due to the increase in blood pressure, lower levels of oxygen, and accompanying changes in blood flow, individuals with sleep apnea are at a higher risk of developing heart disease. This increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and atrial fibrillation.
Type 2 Diabetes
Close to 80% of people with type 2 diabetes suffer from sleep apnea. The link between the two is still being studied, but there is a clear connection. Sleep deprivation can increase insulin resistance and raise your blood sugar levels. If you have sleep apnea and other risk factors for type 2 diabetes, it’s important to see your doctor regularly and undergo screenings, manage your lifestyle choices, and treat your sleeping disorders.
Weight Gain
Sleep apnea also has an impact on your body’s hormones that control hunger. When you’re not getting enough sleep, the hormone ghrelin is produced in excess. Ghrelin can increase your cravings for unhealthy foods like simple carbohydrates and sugar. Conversely, the hormone leptin decreases, which is responsible for sending signals for you to stop eating once your stomach is full. Both of these can lead to weight gain, which can consequently make sleep apnea worse.
Liver Problems
Sleep deprivation caused by OSA can increase the concentration of liver enzymes in your body. This can lead to liver problems, which are worsened by alcohol use and certain medications. In some cases, individuals with sleep apnea have been reported to have fatty liver.
How to Treat Sleep Apnea
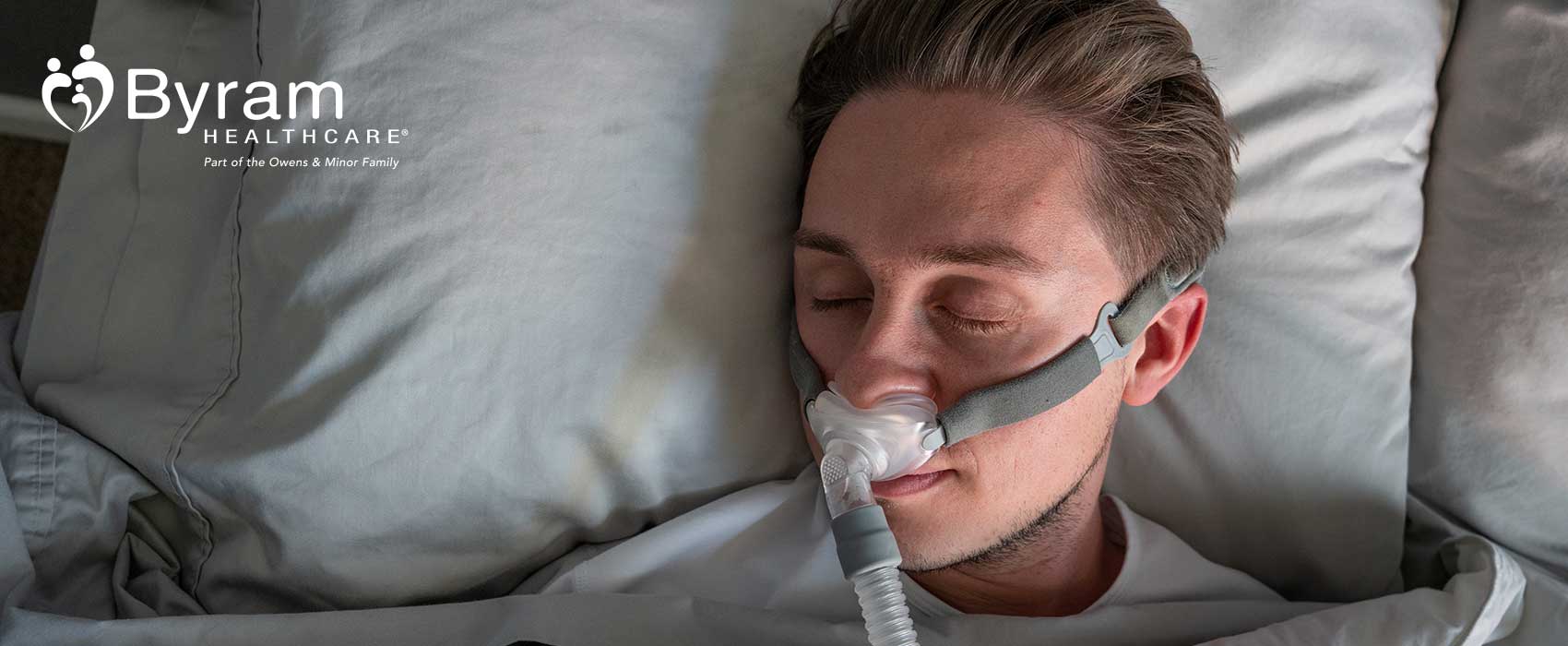
If you experience any symptoms of sleep apnea, contact your doctor to undergo diagnostic testing. There are several treatment options that can help you strengthen your sleeping cycle and reduce the risk of negative outcomes. Some of the most effective treatment options include making lifestyle adjustments, losing weight, altering sleeping positions, or using nasal spray to alleviate congestion. Your doctor may also recommend the use of Positive Airway Pressure (PAP) therapy, which involves wearing a mask over your nose and mouth while sleeping to ensure you receive adequate oxygen and anatomical support. There are various options for PAP therapy, with the most common being a Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machine. In more serious cases, surgical treatment options are available.
About Byram Healthcare and Apria
Since 1968, Byram Healthcare has been helping to improve health outcomes and affordability of care for people managing their chronic conditions at home. For those living with type 2 diabetes, we have a range of continuous blood glucose monitors. We also offer diabetes support and educational materials to give you everything you need for comprehensive care. If you’ve been diagnosed with sleep apnea, Apria offers a comprehensive range of products and services for respiratory therapy and obstructive sleep apnea treatment. Apria is part of the Byram Healthcare family.




